Exterior Materials and Sensor Sensitivity
The Need for Exterior Materials
FSR sensors have an upper plate made of film.
Rather than pressing the sensor's upper plate with hard materials like metal or plastic, it is better to press through a flexible exterior material.
This protects the sensor and stabilizes the contact surface, which also helps reduce signal noise.
Exterior materials are an essential element of FSR sensors, and their composition affects sensor sensitivity.
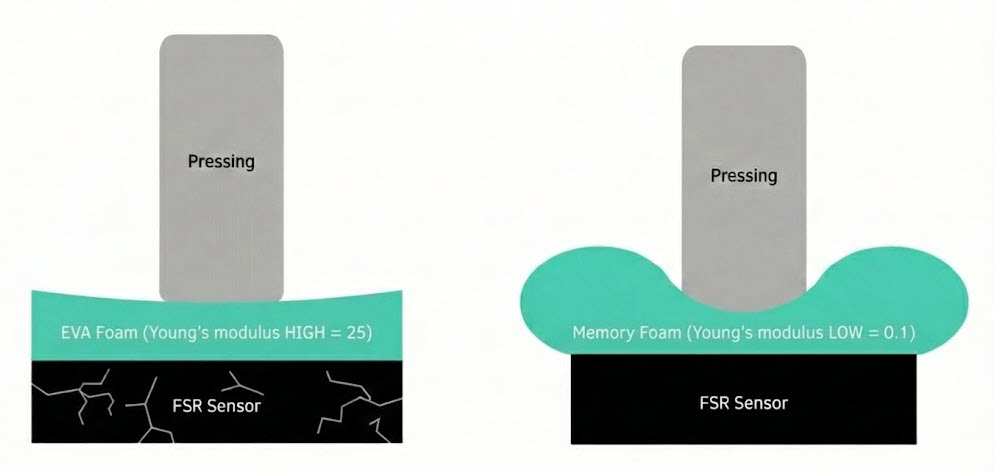
If the exterior material has high Young's modulus or is thick? → The sensor is well protected but responds less sensitively.
Young's Modulus by Exterior Material
| Material | Young's Modulus | FSR Suitability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human fat tissue | 0.001~0.003 MPa | - | Reference only |
| Gel pad | 0.01~0.05 MPa | ★★★ | Very soft |
| Human muscle (relaxed) | 0.01~0.1 MPa | - | Reference only |
| Memory foam | 0.01~0.1 MPa | ★★★ | Excellent recovery |
| Human skin | 0.1~2 MPa | - | Reference only |
| PU Foam (low density) | 0.1~1 MPa | ★★★ | Softest, highest sensitivity (cushion level) |
| Silicone rubber | 1~10 MPa | ★★★ | Excellent durability (used in Marveldex sensors) |
| Natural rubber | 1~10 MPa | ★★☆ | Common |
| Mouse pad | 1~5 MPa | ★★★ | Easy to obtain |
| Kitchen silicone tape | 1~10 MPa | ★★☆ | Easy to adhere |
| Neoprene | 1~10 MPa | ★★☆ | For waterproofing |
| EVA foam | 10~25 MPa | ★☆☆ | Somewhat rigid |
| Plastic (ABS) | 2,000~3,000 MPa | ☆☆☆ | Not suitable |
| Metal (Aluminum) | 70,000 MPa | ☆☆☆ | Not suitable |
1 MPa ≈ 10.2 kgf/cm²
Materials below approximately 10 MPa are suitable as exterior materials for FSR sensors. For applications with heavy loads such as foot platforms or high-pressure jigs, exterior materials in the 10 MPa to 30 MPa range can also be used.
Most FSR sensors released by Marveldex come with silicone material mounted on top of the sensor.
The lower the Young's modulus (softer), the greater the contact area with the sensor, improving sensitivity.
When measuring body pressure with Marveldex FSR sensors, additional exterior materials such as silicone are not necessarily required.