Precision Position Detection
Pressure sensors can be used to recognize precise pressing positions. This is not possible with a single sensor, but position tracking becomes possible when multiple sensors are arranged.
Position Detection Principle
Basic Conditions
- Arrange multiple sensors to measure pressure distribution
- Detection accuracy decreases with larger gaps between sensors
- The pressing area must be larger than the sensor spacing
- Place sensors densely and precisely where deviation typically occurs
Position Detection Precision
| Sensor Array | Sensor Spacing | Theoretical Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| 4×4 | 20mm | ~5mm |
| 8×8 | 10mm | ~2.5mm |
| 16×16 | 5mm | ~1.25mm |
| High Density | 1.2mm | ~0.2mm |
Reference Example
Sensing point spacing: 1.2mm Minimum deviation detection: 0.1mm
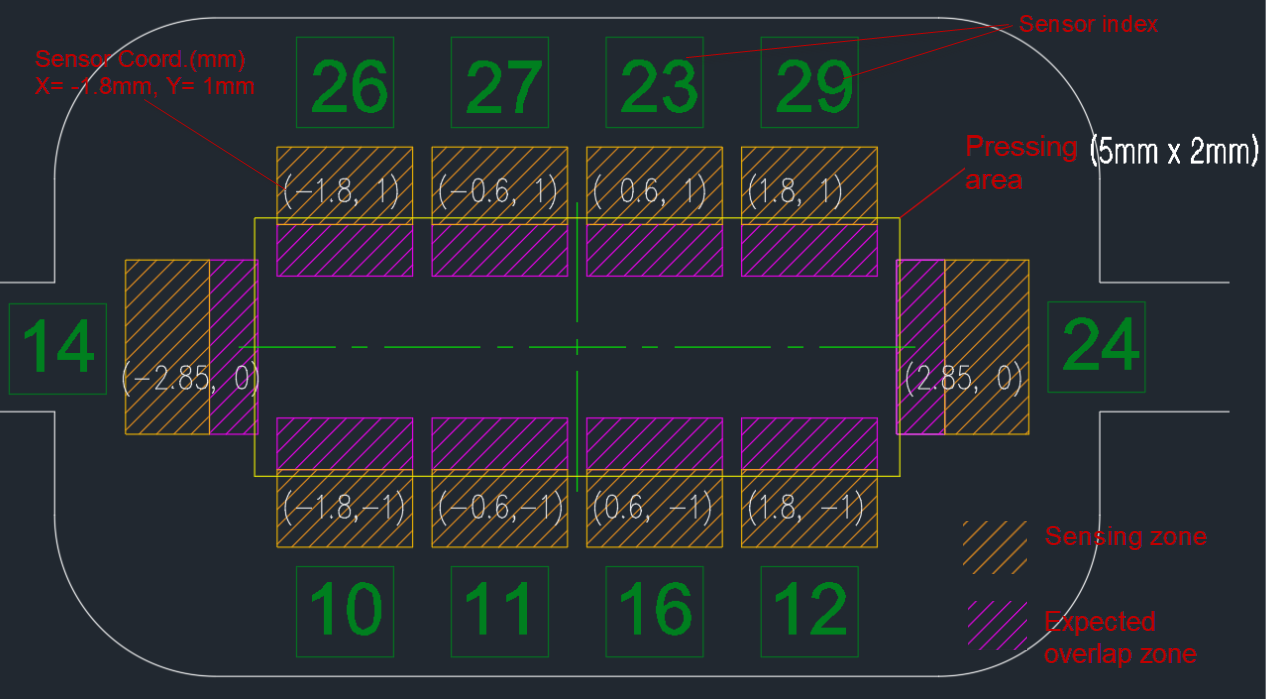
Detectable Actions
Sensor structure for detecting 0.1mm deviation and distortion in the X direction.
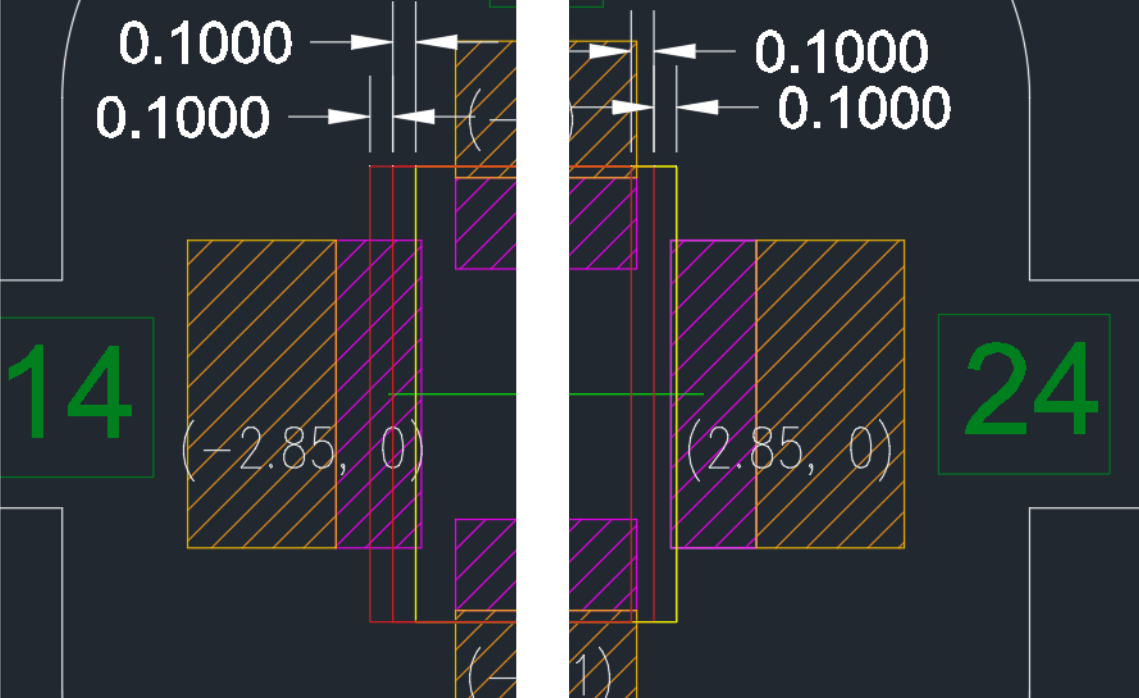
Sensor structure for detecting 0.1mm deviation and distortion in the Y direction.
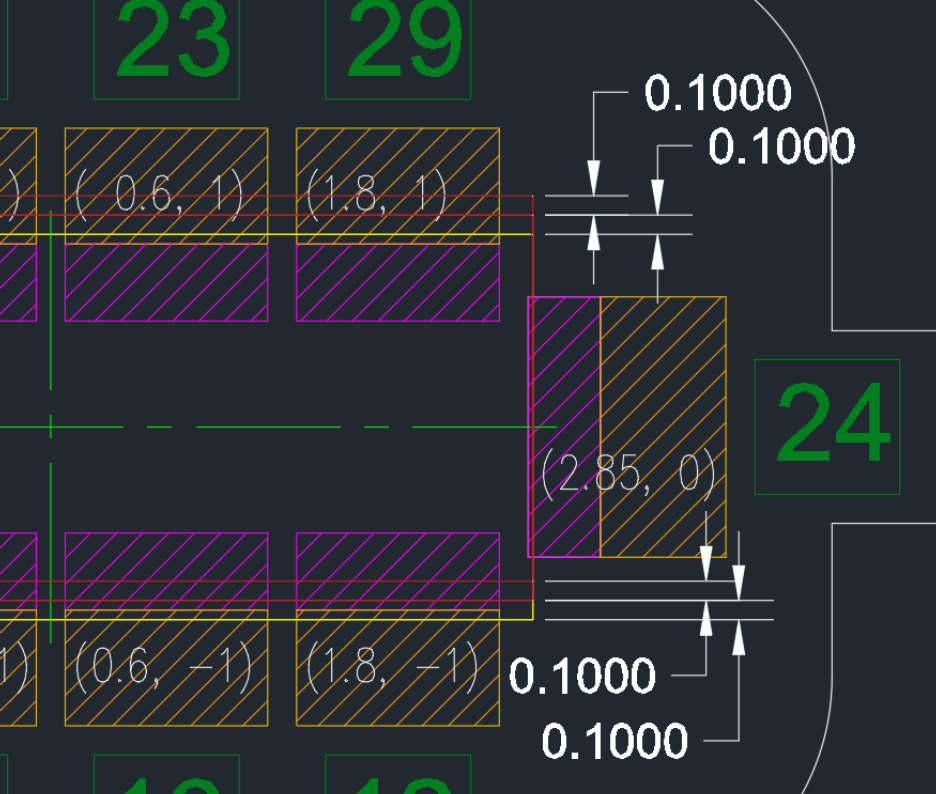
Deviation Detection
- Detecting whether the pressure zone moves outside the sensor range
Twist Recognition
- Detecting rotation/tilting of the contact area
- Detecting which area makes contact first
Center of Gravity Movement Tracking
- Real-time tracking of contact point movement path
Contact Surface Damage Detection
- Estimation based on measurements from multiple contact points
Use Cases
Precision Pressing Equipment
- Detecting position deviation due to equipment aging
- Detecting whether deviation occurs during pressing, even when landing at the correct position
Robotics/Automation
- Verifying gripper grasping position
- Monitoring contact point alignment status
- Inspecting object placement accuracy
Medical/Healthcare
- Plantar pressure analysis (foot pressure distribution)
- Posture analysis systems
- Rehabilitation training feedback
Sports
- Golf grip analysis
- Bat/racket swing analysis
- Balance training systems
Implementation Considerations
Sensor Placement
- Must cover the entire area to be detected
- Closer sensor spacing improves precision
- Consider the trade-off between cost and precision
Sampling Rate
- Fast motion tracking: 100Hz or higher recommended
- Static position verification: 10-50Hz is sufficient
Noise Processing
- Apply moving average filter
- Prevent false detection by setting threshold values
Precautions
- Dead zones: Direct measurement is not possible in gaps between sensors (estimation through interpolation)
- Contact area: Very small contact points (such as pen tips) are difficult to detect
- Pressure threshold: Very low pressure is difficult to distinguish from noise
- Environmental effects: Consider drift due to temperature/humidity changes